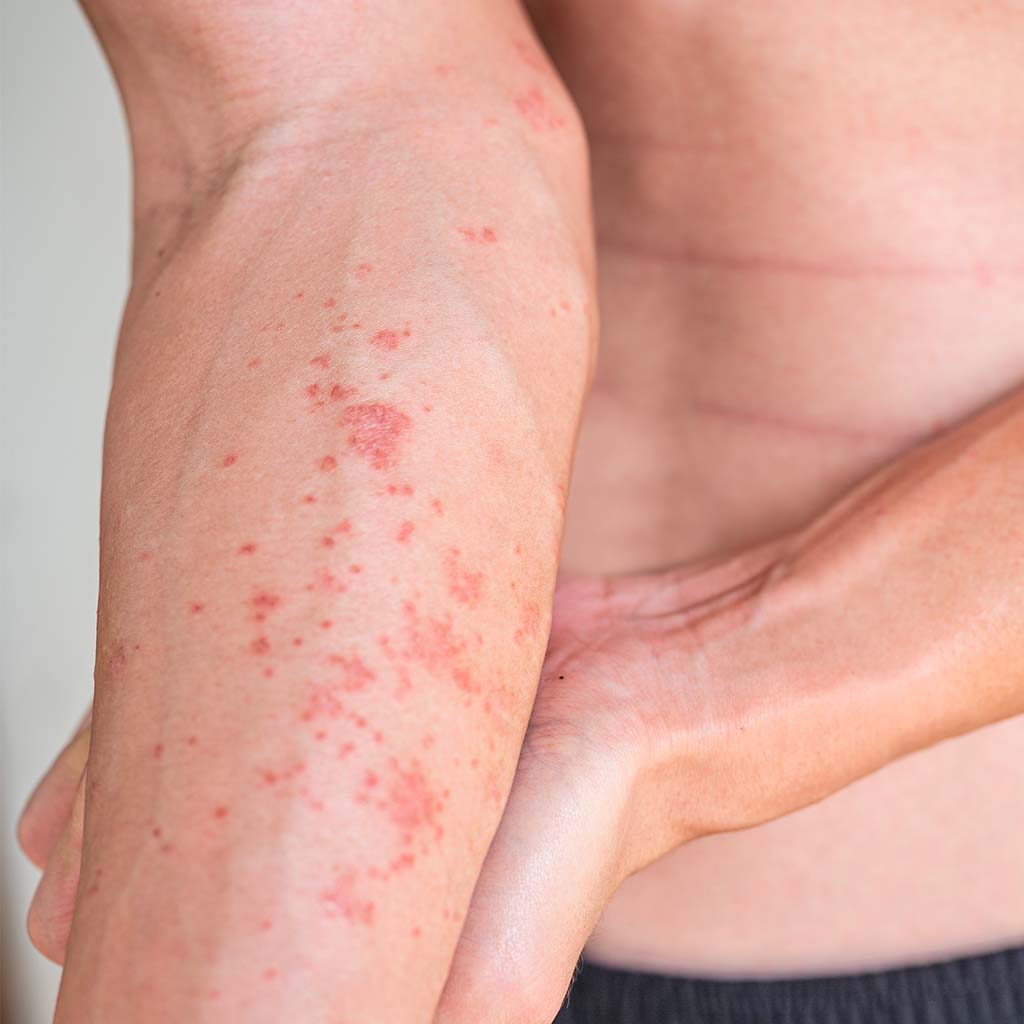
Eczema, a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people across the globe, can be a challenging and frustrating condition to live with. Whether it's an occasional flare-up or a persistent problem, eczema impacts skin health and can have significant effects on daily life. While the exact causes remain elusive, the condition’s hallmark features – itching, redness, and inflammation – are well-known.
In this article, we will dive into the various aspects of eczema, including its causes, symptoms, types, management strategies, and potential treatments to provide a complete understanding of this condition.
What is Eczema?
Eczema refers to a group of inflammatory skin conditions that cause the skin to become itchy, inflamed, and irritated. Often known as atopic dermatitis, 濕疹 is a long-term (chronic) condition that flares up periodically. The skin may also become dry, cracked, or even blistered. While it can occur at any age, it most commonly starts in childhood and can continue into adulthood.
Though eczema isn’t a life-threatening condition, its symptoms can be uncomfortable, and if left untreated, eczema can worsen over time. People living with eczema often deal with persistent itching, which can lead to skin damage from constant scratching, further aggravating the issue.
The Causes of Eczema
The exact cause of eczema is not fully understood, but experts believe a combination of genetic and environmental factors plays a significant role in its development. Here are some key contributing factors:
-
Genetic Factors: Eczema often runs in families, suggesting a hereditary component. People with a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to develop the condition. Certain genes related to the skin barrier function may be altered, leading to a weakened skin barrier.
-
Immune System Dysfunction: Eczema is thought to be an autoimmune-related condition. The immune system in people with eczema tends to overreact to harmless substances, causing inflammation in the skin. The immune system mistakenly perceives environmental factors, like pollen or dust, as threats, leading to skin irritation.
-
Environmental Triggers: External factors, such as allergens, irritants, and climate conditions, can provoke eczema flare-ups. These factors often include pollen, pet dander, mold, dust mites, cold weather, or harsh chemical products.
-
Skin Barrier Defects: People with eczema often have a skin barrier that doesn’t function as well as it should. This makes the skin more susceptible to moisture loss and irritants that can cause inflammation and irritation.
Different Types of Eczema
While atopic dermatitis is the most common form, there are several other types of eczema, each with its own characteristics:
-
Atopic Dermatitis: The most common type of eczema, atopic dermatitis, is often seen in children and tends to appear in areas such as the face, hands, and behind the knees. It is characterized by red, inflamed, itchy patches of skin that may ooze or crust over.
-
Contact Dermatitis: This type of eczema occurs when the skin comes into contact with allergens or irritants. The affected skin becomes red, inflamed, and itchy. There are two subtypes: allergic contact dermatitis and irritant contact dermatitis. Allergic contact dermatitis happens when the skin reacts to substances like certain metals, fragrances, or plants, while irritant contact dermatitis occurs due to exposure to harsh chemicals.
-
Dyshidrotic Eczema: Characterized by small, fluid-filled blisters on the hands and feet, dyshidrotic eczema can be intensely itchy and may cause the skin to crack or peel. The cause of this type of eczema is not fully understood but may be related to stress, allergens, or environmental irritants.
-
Nummular Eczema: This type of eczema presents as round or oval-shaped patches on the skin, typically on the arms, legs, or torso. These patches are often red, itchy, and inflamed and can sometimes become crusted over.
-
Seborrheic Dermatitis: Commonly found on the scalp, face, and other oily areas of the body, seborrheic dermatitis is associated with greasy, flaky skin that may be red and itchy. It is often linked to the overgrowth of a type of yeast found naturally on the skin.
-
Stasis Dermatitis: This type of eczema occurs when poor circulation leads to fluid buildup in the lower legs, typically in people with chronic venous insufficiency. It causes red, itchy, inflamed skin, often accompanied by swelling and varicose veins.
Key Symptoms of Eczema
Eczema symptoms can range from mild to severe and can appear differently in each individual. Common symptoms include:
-
Itching: Intense itching is one of the most bothersome symptoms of eczema. The itch-scratch cycle can cause the skin to become further damaged and irritated.
-
Red, inflamed patches: Eczema is characterized by red, inflamed skin that may become swollen and warm to the touch.
-
Dry and cracked skin: The skin may become excessively dry, leading to cracking, scaling, and flaking.
-
Blisters and oozing: In some cases, eczema can cause small blisters that may burst, leaking a clear fluid and creating crusted patches.
-
Thickened skin: With chronic eczema, the skin may thicken or become leathery due to constant scratching and irritation.
Common Triggers for Eczema
Eczema flare-ups are often triggered by various factors. Identifying and managing these triggers is crucial for minimizing symptoms. Common triggers include:
-
Environmental allergens: Pollen, pet dander, mold, and dust mites are common allergens that can trigger eczema flare-ups.
-
Irritants: Harsh soaps, fragrances, cleaning products, and certain fabrics like wool or synthetics can irritate sensitive skin.
-
Extreme weather: Cold, dry air or excessive humidity can worsen eczema symptoms.
-
Stress: Emotional stress is a known trigger for eczema, as it can trigger inflammatory responses in the body.
-
Food allergies: Some individuals with eczema may experience flare-ups in response to certain foods, such as eggs, nuts, or dairy products.
Treatment and Management of Eczema
Although there is no cure for eczema, there are several ways to manage and control the condition effectively. Treatment options typically focus on relieving symptoms, preventing flare-ups, and maintaining healthy skin.
-
Moisturize Regularly: Keeping the skin moisturized is one of the most important steps in managing eczema. Using thick creams, ointments, or oils can help restore the skin's natural barrier, keeping it hydrated and preventing dryness and cracking.
-
Topical Steroid Creams: These medications reduce inflammation and help alleviate itching. Depending on the severity of eczema, doctors may recommend mild to strong corticosteroid creams or ointments.
-
Non-Steroidal Topical Medications: Topical calcineurin inhibitors, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, are often prescribed for sensitive areas like the face and eyelids. These medications help reduce inflammation without the use of steroids.
-
Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines can help relieve itching and promote sleep, especially if the symptoms worsen at night.
-
Phototherapy: For severe cases, light therapy (phototherapy) may be used to expose the skin to controlled ultraviolet light, helping to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms.
-
Biologic Treatments: For those with moderate to severe eczema that doesn't respond to other treatments, biologic medications like dupilumab (Dupixent) are becoming increasingly available. These treatments target specific molecules in the immune system to reduce inflammation.
-
Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding environmental triggers is key to preventing flare-ups. This may include avoiding certain allergens, using gentle skin care products, and wearing breathable clothing.
Conclusion
Eczema is a challenging condition, but with proper care and treatment, most individuals can manage their symptoms effectively. Whether through moisturization, medications, or lifestyle adjustments, there are various options available to minimize the impact of eczema on daily life. By understanding the condition and working with healthcare professionals, individuals with eczema can find the right approach to maintaining healthy, comfortable skin.
